WATCH OUT FOR KEY INDICATORS OF FINANCIAL DISTRESS, SIGNS OF FINANCIAL TROUBLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Watch Out For Key Indicators of Financial Distress, Signs of financial trouble.
As a business owner, it is essential to be aware of the critical indicators of financial distress. Management should know these indicators when operating an organization. Knowing vital indicators will help you take appropriate action before financial distress occurs. You know from business failure, restructurings, and bankruptcy filings.
An indicator of financial distress is if your company is consistently losing money. If your organization is in the red month after month, it’s a sign that something is wrong, moving toward a possible bankruptcy. Another indicator is if you’re financial trouble paying your bills on time. Suppose you’re constantly juggling which invoices to pay and when it’s a sign that your business is in financial difficulty.
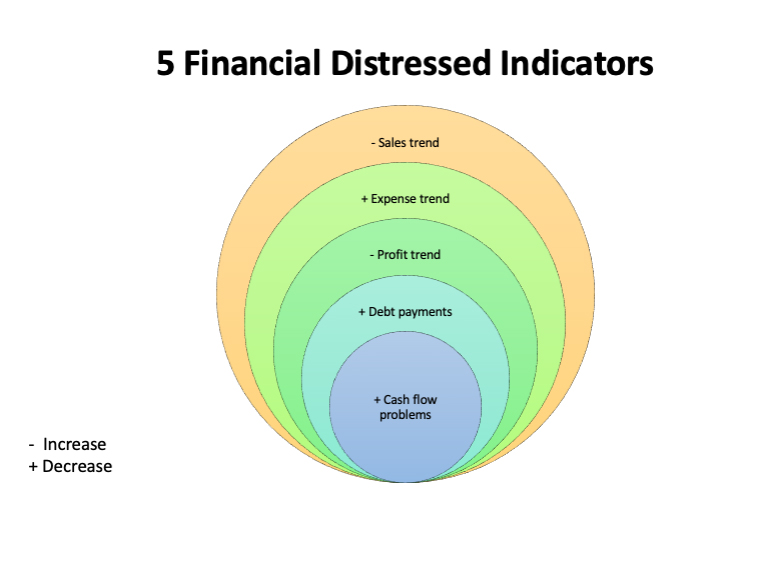
FIVE KEY INDICATORS OF FINANCIAL DISTRESS
In this blog post, we will discuss five key indicators that you should watch out for. Avoiding financial burden and insolvency filings is critical with the possibility of a recession and economic downturns. Keep reading to learn more!
You must, as management, control resources, keep customers happy, and manage growth, to avoid failure. Think about the cost of financial distress and analyze your financial statements. What are the five key indicators of financial distress that management should watch out for?
The first indicator of financial distress
INDICATOR 1: DECLINING SALES TREND
The first key indicator of financial distress is declining sales. If your company’s sales are steadily declining, it could be a sign that your business is in trouble. Henceforth, you should monitor your sales numbers closely and look for any red flags.
REVIEW MARKETING COSTS THAT IMPACT REVENUE
The Key is reviewing marketing efforts. Sales are about customers. In controlling marketing, you should look at the industry, company service, and product offerings. Revenues are primarily based on the services offered, which impact customers. You have to look are the resources thrown at attracting customers. That is to say, you, as management, have to look at the effective cost of the money you paid that impacts income and the top line. Consequently, reduced income is an indicator.
INDICATOR 2: INCREASING EXPENSE TREND
The second key indicator is increasing expenses. If your business expenses are rising faster than its revenues, it could signify financial distress. You should closely monitor your expenses and look for areas where you can cut costs.
REVIEW OPERATIONAL AND ADMINISTRATIVE COSTS THAT IMPACT EXPENSES
Review the percentage of marketing expenses relative to the industry. Several other reasons may exist that impact the efficacy of the company’s products.
INDICATOR 3: DECLINING PROFITS TREND
The third key indicator is declining profits. Financial distress could be a sign if your business’ profits are falling. You should monitor your company’s profit margins closely and look for any red flags or signs of financial trouble.
INDICATOR 4: INCREASING DEBT PAYMENTS
The fourth key indicator is increasing debt. If your business’s debt rises, it could signify financial distress. You should monitor your company’s debt levels closely and look for any red flags.
Look at the industry as possibly restructuring the company’s financial obligations.
INDICATOR 5: CASH FLOW PROBLEMS
The fifth and final key indicator of financial distress is cash flow problems. If your business has difficulty paying its bills on time, it could signify financial distress. You should monitor your company’s cash flow closely and look for any red flags.
If you notice any of these key indicators of financial distress, you should take action immediately. To clarify, the sooner you address the problem, the better your chance of saving your business.
ARE YOU ASSESSING FINANCIAL TROUBLE?
Watch out for these five critical financial distress (financial problems): declining sales, increasing expenses, declining profits, rising debt, and cash flow problems. If you notice these red flags, take action immediately to save your business. Conversely, management must pivot the organization to reduce high-interest payments and fixed costs and mitigate illiquid assets and other obligations.
THE IMPORTANCE OF READING FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Reading your company’s financial statements regularly is essential to avoid financial distress. Financial statements can give you a clear picture of your company’s financial health. Above all, financial reports can help you spot any red flags that may indicate financial trouble.
Ensure you understand your financial statements and watch out for any red flags. If you see any warning signs, take action immediately to save your business.
When reviewing your financial statements, there are three key documents that you should focus on: the balance sheet, the profit and loss statement, and the cash flow statement.
REVIEW THE BALANCE SHEET – THE STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION
The balance sheet shows a snapshot of your company’s financial position at a specific time. It lists your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. Consequently, the balance sheet can help you identify any financial position red flags.
You should review the company’s liquidity and leverage position. The liquidity indicates the company has enough cash to pay its short-term debts. Henceforth, the leverage position suggests the company’s debt relative to its equity is considered solvency.
It would be best if you kept an eye on liquidity ratios. Consequently, the current and quick ratio or acid test are two crucial ratios in assessing financial trouble.
THE CURRENT RATIO
A current ratio is a measure of a company’s liquidity. It is calculated by dividing a company’s current assets by its current liabilities. A current ratio of less than one indicates that the company may have difficulty paying its short-term debts.
THE QUICK RATIO
The quick ratio is another measure of a company’s liquidity. It is calculated by dividing a company’s quick assets by its current liabilities. Quick assets are liquid assets that can be quickly converted to cash, such as cash and marketable securities. A quick ratio of less than one indicates that the company may have difficulty paying its short-term debts.
It would be best if you also kept an eye on leverage ratios.
LEVERAGE RATIO – THE DEBT TO EQUITY RATIO
The debt to equity ratio measures a company’s financial leverage obligations. It is calculated by dividing a company’s total liabilities by its total equity. The debt to equity ratio of more than one indicates that the company has more debt than equity.
Consequently, this means the company is more leveraged and may be at a higher risk of financial distress.
LEVERAGE RATIO – THE DEBT TO ASSETS RATIO
The debt to assets ratio is another measure of financial leverage. It is calculated by dividing a company’s total liabilities by its total assets. A debt to assets ratio of more than one indicates that the company has more debt than assets. Thus, this means the company is more leveraged and may be at a higher risk of financial distress.
REVIEW THE PROFIT AND LOSS STATEMENT – THE INCOME STATEMENT
The profit and loss statement shows your company’s revenue, expenses, and profits over some time. It can help you identify any financial red flags.
Moreover, you should keep an eye on two essential ratios: the gross margin and the operating margin.
THE GROSS MARGIN RATIO
The gross margin ratio is a measure of profitability. It is calculated by dividing a company’s gross profit by its revenue. The gross margin ratio indicates a company’s profit before paying its operating expenses.
A low gross margin ratio may indicate that the company is not generating enough revenue to cover its costs. This could be a financial red flag. Therefore, you are able to determine whether the product or service sold was sufficient to meet product and service costs.
THE OPERATING (EBITDA) MARGIN RATIO
The operating profit margin is a measure of a company’s financial health. It is calculated by dividing a company’s operating profit (EBITDA – earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) by its total revenue. A gross profit margin of less than one indicates that the company is not making a profit.
After reviewing the margins, assessing the interest coverage is essential. Hence, the following margin measures profitability.
INTEREST COVERAGE
The interest coverage ratio measures a company’s ability to make interest payments. It is calculated by dividing a company’s earnings before interest and taxes by interest expenses. An interest coverage ratio of less than one indicates that the company may have difficulty making its interest payments.
High-interest payments are a red flag of possible financial strain, consequently is the cost of financial distress.
REVIEW THE CASH FLOW STATEMENT
The cash flow statement shows how much cash a company has on hand. Keeping an eye on the cash flow statement is vital because it can help you identify any financial red flags and the cost of financial distress.
You should watch out for any red flags in the cash flow statement. Red flags can include a negative cash flow from operating activities. As most financial statements use the accrual accounting method, converting transactions to cash is critical. Consequently, accrual accounting tells a story of the cash use of the organization.
The cash flow statement measures the cash from three activities: Cash flow from operating activities, cash paid for investing activities, and cash flow from financing activities. Accordingly, measuring the movement of cash is critical in the determination of financial distress.
CASH FLOW FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES
You should review how much cash is generated from the company’s operations. The cash flow from operating activities measures the amount of money a company generates from its normal business operations. This is important to watch because it can help identify financial distress.
If a company is generating a negative cash flow from its operations, consequently, it means that it is not making enough money to cover its costs. In addition, this is a financial red flag.
CASH FLOW FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES
You should also review how much cash is being paid for investing activities. Investing activities include things like buying new equipment or selling investments.
If a company is paying more cash for investing activities than it is generating from its operations, it may be in financial distress.
Cash flow from financing activities
The cash flow from financing activities measures the amount of cash that a company has borrowed. If a company borrows more money than it is generating from its operations, it may be in financial distress. Consequently, the need for new equity may be necessary.
HOW CAN YOU GET HELP IF YOU’RE STRUGGLING TO KEEP YOUR BUSINESS AFLOAT FINANCIALLY?
If you’re struggling to keep your business afloat financially, you can do a few things. You can try to negotiate with your creditors for more favorable terms. You can also explore ways to cut costs and increase revenues. And finally, you can seek financial assistance from investors or the government.
Another key indicator of financial distress is high levels of debt. If your business has a lot of debt, it can be challenging to make ends meet. This is because you’ll have to use a large chunk of your revenue to pay off debts, leaving less money for other expenses. Additionally, if you’re having trouble getting loans or lines of credit, it’s another sign that your business is in financial distress.
The last two indicators of financial distress are trouble meeting payroll and employee turnover. If you’re having difficulty paying your employees on time or keeping them happy, it’s a sign that your business is in trouble. Additionally, if you’re losing a lot of employees, it’s another indication that something is wrong.
CONCLUSION
So, what can you do to keep your business afloat if there is another recession and the company faces a financial burden (experience financial distress)? The best thing you can do is be proactive and watch for the five signs we talked about. Furthermore, keep an eye on your financial statements, restructure any high-interest payments, and ensure you are aware of any red flags. If things start looking bad, don’t wait – take action! Follow me and link this blog to your writings so that others can learn how to stay out of trouble during tough economic times.
